Getting Started
Defining the Interface Protocol
Creating the Server
Creating the Client
Now, lets explore how to use IPC between components.
Covered in this topic:
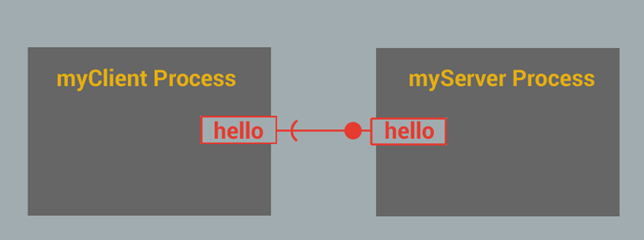
Here's what it looks like at runtime:
When we show the static view of components inside executables, it looks like this:
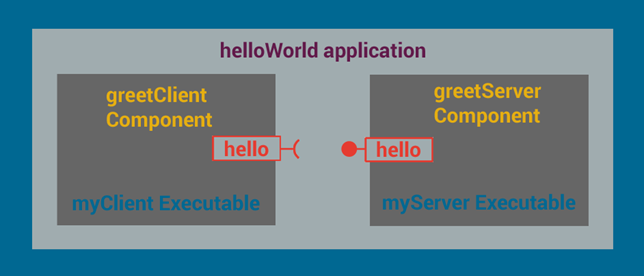
Note that each interface has
In our example, the client and server both use the same friendly name "hello" for their interfaces, and of course, they both must use the same protocol, or they wouldn't be able to communicate with each other.
First, let's create a directory for our little project and change directories into there:
$ mkdir helloIPC $ cd helloIPC
Next, we define the interface protocol to be used between the client and the server.
To create our function-call API, we create a definition file called "greet.api".
$ gedit greet.api
Put the following inside greet.api:
FUNCTION Greet ( );
This declares a function called "Greet" that takes no arguments and returns nothing.
Next we create a server component called "greetServer" that offers a greeting service called "hello" that can be accessed using our simple "greet" API. We do this by creating a file called "Component.cdef" in a new directory called "greetServer".
$ mkdir greetServer $ gedit greetServer/Component.cdef
greetServer/Component.cdef should contain the following:
export:
hello = greet.api
sources:
greetServer.c
This declares that the component named "greetServer" (the name of the directory is the name of the component) exports a service called "hello" that is accessed using the API defined in "greet.api", where the source code can be found in the file greetServer.c.
To implement the server (in C), create a file "greetServer/greetServer.c":
$ gedit greetServer/greetServer.c
Make it contain the following:
#include "legato.h" #include "interfaces.h" void hello_Greet(void) { LE_INFO("Hello world."); } COMPONENT_INIT { hello_StartServer("hello"); }
The file "interfaces.h" will be auto-generated based on the contents of greet.api and greetServer's Component.cdef. It will contain a prototype of the function hello_Greet(), which we implemented in greetServer.c.
The function hello_Greet() will be called when a client binds to our "hello" service and calls the function Greet(). The name "hello_Greet" follows this pattern:
<export-name> '_' <api-function-name>
The <export-name> is the name given to the exported interface. In our example, it is the name "hello" before the '=' in the line "hello = greet.api".
In this simple example, it's starting the service by calling the auto-generated function hello_StartServer ("hello"). This parameter will go away in the future, but for now must match the function prefix.
Now that we have a server, let's create a client to use its service. First, create a directory for the greetClient component and a file in it called "Component.cdef".
$ mkdir greetClient $ gedit greetClient/Component.cdef
greetClient/Component.cdef should contain:
import:
hello = greet.api
sources:
greetClient.c
To implement the client using C, create a file called "greetClient/greetClient.c":
$ gedit greetClient/greetClient.c
Make it contain the following:
#include "legato.h" #include "interfaces.h" COMPONENT_INIT { hello_StartClient("hello"); hello_Greet(); }
The "interfaces.h" file that the client includes is a different one than the one that the server uses. This one is specially generated for the client based on the contents of greetClient/Component.cdef and greet.api.
In the client, we use the component initializer to call hello_Greet() at start-up.
Copyright (C) Sierra Wireless, Inc. 2014. All rights reserved. Use of this work is subject to license.